The SAP Software Company was founded in 1972 in Walldorf, Germany. It’s a well-known corporation that offers application software and helps companies reach their full potential in many industries. Its state-of-the-art Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning, and analytics solutions assist clients in becoming smarter enterprises. The company’s extensive selection of apps and services enables our clients to run successful businesses, adapt quickly, and make a difference.
The organization provides services to industries such as banking, retail, government, automotive, aerospace and defense, and others. In these industries, several SAP Jobs for Freshers are available, and those who land these positions are rewarded fairly well. Freshers Jobs will guide freshers with the SAP interview questions with sample answers.
Interview Process
Applicants who wish to work for SAP must familiarize themselves with the SAP Interview Process and make appropriate preparations. In the next few parts, we will examine the SAP interview process, the application procedure, and the selection criteria.
The hiring process begins after a candidate files their SAP application and has their resume shortlisted. The steps involved in becoming a member of SAP Labs are as follows.
- Pre-Assessments
- Technical Interview Round
- HR Interview Round
Pre-screening calls
After a candidate’s resume is selected for a position, a SAP recruiter will call them to discuss the opportunity and the following steps. The candidate’s resume will also be examined, and information such as employment history, education, address, and salary will be confirmed. The candidate must complete the following rounds of the SAP Recruitment Process to be considered for a career at SAP.
Technical Interview Round
If the candidates make it through the initial step of the SAP Hiring Process, they will be invited to technical interviews for undergraduate SAP job opportunities. They will have to participate in two or three rounds of interviews with technical personnel. The candidate must have a strong technical background, particularly in programming and core areas, to pass the technical rounds. This round of questions will center on the candidate’s job history. When attending a technical interview, the SAP Interview Questions will be based on Java, OS, programming languages, SQL, coding, and other topics. The candidate may need to work through issues.
HR Interview Round
The HR interview is the last phase of the interview process, during which an HR examiner investigates the candidate’s background, education, work history, conduct, leadership values, and other factors. The candidates will be asked subjective questions about news and current affairs in addition to technical ones.
HR interview Questions
- Tell me about yourself.
I am a [name your degree] graduate from [name your college/university]. I acquired a solid foundation in [name pertinent courses or coursework] over my academic career, which drove my enthusiasm for [name your sector or area of interest, such as software development or data analysis]. In addition, I took an active part in extracurricular activities such [include any organizations, initiatives, or leadership positions that are pertinent]. I gained useful time management andteamwork skills from these experiences.
- What motivates your interest in pursuing a career in the field of information technology?
The information technology industry truly excites me for a number of reasons. It’s a vibrant, constantly changing sector that offers fresh chances for creativity as well as new obstacles. Because of this ongoing change, I will have the opportunity to continue learning and developing throughout my career.
- Why do you want to work at Tech Mahindra?
The idea of working with SAP excites me for a number of strong reasons. First off, SAP is well known in the IT sector for its innovation and quality. The company’s dedication to keeping up with technical changes has really pleased me, and it fits in well with my desire for lifelong learning and development.
- Would you be willing to move to different locations across India if required?
I would not hesitate to relocate to any part of India if it became necessary for the job. I see it as a chance to travel, see a variety of new things, and successfully support the objectives of the business. As I continue on my professional adventure, I’m looking forward to embracing new challenges and adjusting to new situations.
- What Salary expectations do you have in mind?
In terms of pay expectations, my main priority is to identify the ideal chance to launch my career and get significant experience. I believe SAP provides competitive pay packages that are in line with the demands of the position and industry norms. My main objective is to successfully contribute to the company’s success, and I’m sure that as my career progresses, the salary will commensurate with my abilities and achievements.
SAP also called System Applications and Products in Data Processing is the most demanded and leading Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software package that is used in the efficient management of the company’s resources. The SAP system offers a wide array of fully integrated modules that comprehensively address various aspects of business management. A significant benefit of adopting SAP as the company’s ERP system lies in its exceptionally high level of integration among its applications, guaranteeing data consistency across both the system and the organization.
Technical Interview Questions
Let’s look into some frequently asked sap interview questions with sample answers for freshers.
- Could you please define SAP?
SAP, which stands for System, Application, and Products in Data Processing, stands as the most demanded and leading ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software package, renowned for its effectiveness in resource management within a company.
- What are NetWeavers and the advantages of using it?
NetWeaver is known as an integrated technology platform that enables users to run various products from mySAP suite on a single instance, which is known as SAP Web Application Server (SAP WEBAs).
An advantage of using NetWeaver is the user can access SAP data using the web (HTTP protocol) or from a mobile device. This method will lessen the cost of training clients on SAP Client-side GUI.
- Define Pooled tables in SAP.
A pooled table is present in the SAP ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming) dictionary that stores control data. The polled table is an SAP proprietary creation that consists of a many-to-one relationship with tables within the SAP database. The SAP data dictionary can hold multiple smaller tables. This will result in the reduction of the space and resources needed at the database level. The main use of pooled tables in SAP is for system data maintenance.
- Define variables in SAP.
Variables are defined as query parameters set in the definition of parameter query, and the values will be assigned after the query is entered into the workbooks. There are diverse types of variables that are used in different applications. Some variables are text, formulas, replacement path, user entry type, hierarchies, hierarchy nodes, characteristics variables, processing types, etc.
- Define the two types of services used to deal with communication in SAP.
The 2 types of services that are used to deal with communication are:
- Gateway Service: Gateway Service allows communication between SAP R/3 and external applications by using the CPI-C protocol.
- Message Service: Application servers will use the Message Service to exchange short internal messages.
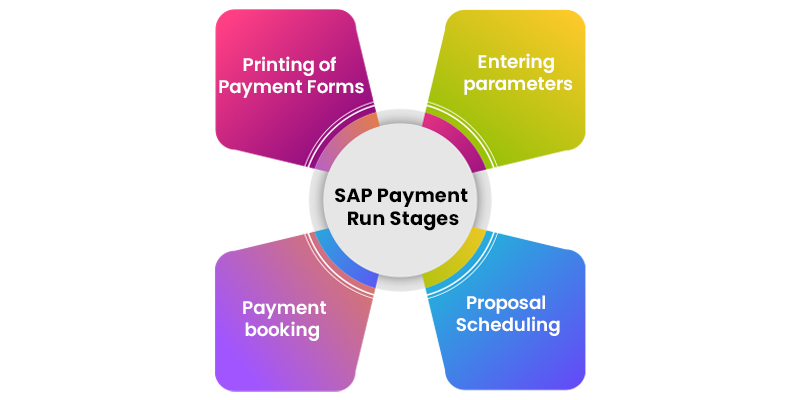
- Explain what are the standard stages of the SAP Payment Run.
The Standard stages of the SAP on SAP Payment Run execution are:
- Entering parameters: This method will involve entering company codes, methods of payments, vendor accounts, etc.
- Proposal Scheduling: In this method, the system will provide a list of invoices to be paid
- Payment booking: The payment Booking method includes the process of booking the actual payment into the ledger
- Printing of Payment Forms: This method involves the payment forms printing.
- Explain the importance of ODS (Operational Data Store) in BIW (Business Warehouse Information).
An ODS is defined as an Object that supports debugged transaction data storage on a document level. It will generally define a combined dataset from a single or multiple InfoSources. The user can analyze this dataset with an InfoSet Query or BEx Query. Users have the ability to apply delta updates to ODS (Operational Data Store) Objects, which can then be propagated to InfoCubes and other ODS Objects within the same system or even across different systems.
Some sap interview questions and answers will be in the form of an explanation. Some questions in that format are given below. Freshers can check out the latest job vacancies in fresher jobs in Delhi.
- Could you please explain what ERP is?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a computer-based integrated software system extensively employed by businesses to efficiently oversee their day-to-day operations, encompassing manufacturing, supply chain, financials, services, and various other processes. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring seamless information dissemination and workflow management across different departments within a company or enterprise. Originally, ERP primarily focused on planning and managing essential business functions such as production and financial operations. Nowadays, it serves as a vital tool for integrating information across the entire organization. SAP emerged as one of the first companies to deliver top-tier ERP solutions and develop standardized software developed for business needs. Other examples of ERP systems available in the market include Microsoft Dynamics, JD Edwards, Siebel, PeopleSoft, and Baan. ERP software encompasses all fundamental business domains, including Production, Human Resources, Financials & Accounting, Planning, Inventory Management, Reporting, Sales & Marketing, CRM.
Some sap interview questions can be like explaining a concept, including its functions. One such question with a sample answer is given below.
- Explain about the uses of SAP.
- SAP helps organizations and companies in boosting productivity and profit, frequently receiving modifications and developing sustainably.
- Companies will design SAP software for the usage of large, mid-sized, and smaller businesses. Each and every process of the business will be mapped and designed by using standard applications, platforms, technologies, and industry solutions. One of the functions of SAP is to collect the data and process it on a single platform. The data can be production, customer satisfaction, or raw material purchasing-related data.
- The user can use SAP solutions from the cloud, or it can be installed on-premise in their place by helping companies analyze and design the entire chain of value efficiently.
- SAP solutions can be used in the process of creating forecasts, like the one used in predicting how revenues will develop in the next half-year or, when to repair a machine, etc.
- In addition, SAP enables customers to flawlessly link operational data on the process of business with experimental data on emotional factors such as purchase experience or customer feedback. It provides the company with a better understanding of the customer’s needs and responds appropriately.
- Define Metadata, Master data, and Transaction data.
- Meta Data: Meta Data provides information about the structure of the given data, database table objects, etc. For instance, the ABAP Dictionary will give all the required information within RDBMS.
- Master Data: It is composed of information on whatever a company does and how it can be defined over competitors and business units. It helps to visualize the whole business view. Master Data contains key information like the information of the customers, employee details, materials, etc. For instance, let’s say a customer had ordered 5 units of the company’s product. Instead of asking for the customer’s address 5 times, it can be easily referred from the Master data, which contains all the customer details.
- Transaction Data: It consists of day-to-day transaction data. For instance, let’s say the details of the daily production that are related to the material, imported materials, daily transactions, etc., are stored in Transaction Data.
- Define BEx in SAP.
- BEx stands for Business Explorer, which is a tool that is provided by SAP SE, a software company that supports the entry of data in Business Warehouse (BW) Integrated Planning and in creating planning applications.
- BEx helps the end-user in locating reports, executing the query, analyzing the information, and viewing the reports. Suppose one of the employees has authorization access. In that case, they can evaluate the current or historical data at various levels of detail and from diverse perspectives, both on the Web in Microsoft Excel and the portal.
- The components of BEx are BEx Map, BEx analyzer, and BEx Web. The queries that are presented in the workbook can be stored in their corresponding roles within the BEx browser.
- BEx Information Broadcasting will enable the distribution of the objects that are created with the Business Explorer using email. The objects can be distributed either as a document that contains historical data that were calculated previously or as a link with live data.
- Explain SAP PI/PO (Process Integration/Process Orchestration).
SAP PI/PO allows users to facilitate the integration of solutions between SAP systems and both SAP and non-SAP systems. By this, data between other systems can be synchronized seamlessly. For instance, Let’s say that the user uses the SAP ERP system and wants to integrate it with the CRM system. This integration can be easily done using PI, which permits the user to perform the integrations easily, using a standard tool that allows the user to maintain diverse connections in a single place.
By the use of SAP PI/PO, it is possible to synchronize data to a warehouse system. For instance, Let’s say that the user wishes to send all the information that is related to the orders, such as how they are used, which one of them is being produced, and when they need to be shipped.
Users can work effortlessly by using SAP PI/PO. This happens because developers and organizations have a single tool that can be used for various integration varieties instead of using multiple tools for smaller tasks.
- What is LUW (Logical Unit of Work)?
A Logical Unit of Work (LUW) is referred to as a series of database operations that has to be either completely executed or not to be executed. LUW enables the integrity of the database. The database is in a correct state when a Logical Unit of Work has been successfully concluded. If any error occurs in an LUW, the modifications that are made to the database will be canceled, and the database will return to the previous state as before the LUW started.
An LUW will begin:
- Each time you begin a transaction.
- When the changes made to the database by using the previous LUW were confirmed.
- When the changes made to the database by using the previous LUW were canceled.
An LUW will end:
- At the time when the changes made to the database were confirmed.
- At the time when the changes made to the database have been canceled.
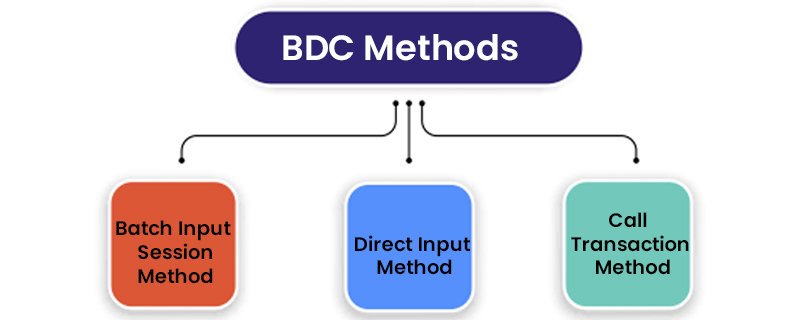
- What is BDC (Batch Data Communication)? How many methods of BDC are present?
The function of Batch Data Communication is to transfer data from the Non-SAP system to the SAP R/3 system. It is possible to add a large amount of data into the database of SAP tables rather than entering it manually. By SHDB transaction to record the movement of the cursor.
The cursor movement can be noticed by the SAP software, and the data can be sent or stored in an appropriate position according to our Excel or flat file. The 3 methods of BDC that can be used for transferring the data.
- Batch Input Session Method: The function of this method is to be used in ABAP programming when no other method exists. The online transaction process will be simulated, and the data transfer will be done in the same way as it is done online. By using SHDB, batch input sessions will be created that contain all the data and screens, and then they are processed. If the user has made any changes to the screen, then they have to add these screens to the program; otherwise, BDC will fail.
- Direct Input Method: In the Direct Input method, the input file data is directly transferred to the SAP database. In this method, function modules will be used to complete the task.
- Call Transaction Method: It initiates asynchronous processing of data, and only a small amount of data is transferred. The data will be updated automatically and will speed up the process. If the user is using this method, errors must be handled properly if the user is using this method.
- Explain about SAP services.
Some of the SAP services are:
- SAP Application Management Services: This service includes the development of applications, implementation, integration, testing, monitoring, and backup and recovery.
- SAP Platform Modernization: In this service, the modernization approach will convert SAP into a dynamic digital core that is ready to fit into regularly changing market conditions and customer’s needs.
- SAP S/4 HANA Migration and Transition Services: This service offers integrated business planning and digital transition strategies for migrating to S/4 HANA, facilitating a smooth transition. The user’s aim is to transfer the features while implementing technology that supports the needs of a business.
- SAP S/4 HANA Implementation Services: This service empowers businesses to meet the demands of the digital economy.
- SAP Technology Platform & Infrastructure Services: This service verifies the security of your ERP platforms, whether they are existing SAP platforms, part of S/4 HANA, or part of a cloud migration/implementation.
Some sap interview questions can be like explaining about a concept including its components. One such question with a sample answer is given below. To know more about the latest updates click SAP Jobs for freshers.
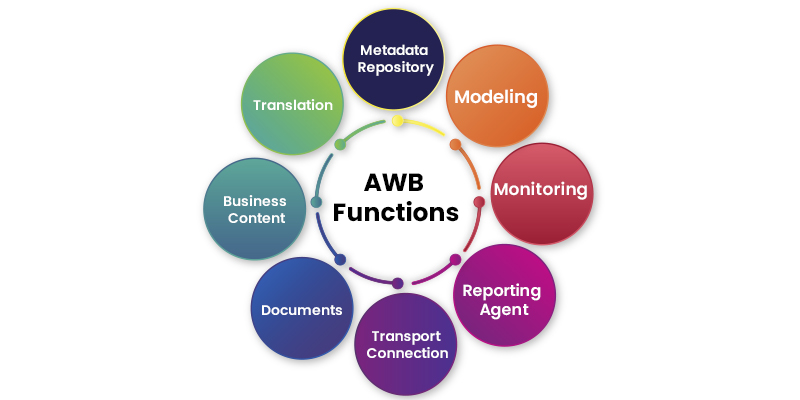
- What is AWB and its functions?
The Administrator Workbench (AWB) serves as a valuable tool for overseeing, maintaining, and supervising all processes associated with the staging and data processing within SAP Business Information Warehousing. Additionally, it facilitates the creation, modification, and customization of various metadata objects within the Business Warehouse.
The functions of the Administration Workbench (AWB) in SAP BW encompass:
- Modeling: This function is utilized for crafting and upkeeping metadata objects relevant to data staging and processing within SAP Business Warehouse (SAP BW). Arranged in a hierarchical tree structure format, these objects enable convenient access to maintenance dialogs via the context menu. To access the Modeling functions, you can use transaction RSA1.
- Monitoring: The Monitoring function is instrumental in overseeing and managing data loading and related processes within SAP BW.
- Reporting Agent: The Reporting Agent tool enables the scheduling and execution of reporting functions in the background.
- Transport Connection: This area is valuable for transferring newly created or modified objects within BW systems. For example, it facilitates the transportation of objects from development servers to testing servers and, subsequently, to production systems.
- Documents: In this function area, you can insert, search, and create links for one or more documents in accordance with specific formatting, languages, and versions tailored to SAP BW objects.
- BusinessContent: Business Content offers pre-configured data models based on metadata, essentially comprising SAP-defined objects available in the delivered version.
- Translation: This function allows for text translation for SAP BW objects.
- Metadata Repository: Within the metadata repository of HTML, SAP BW metadata objects and their associated links to other objects are centrally managed through an integrated metadata repository browser.
Answers to some sap interview questions for freshers have to be explained in-depth.
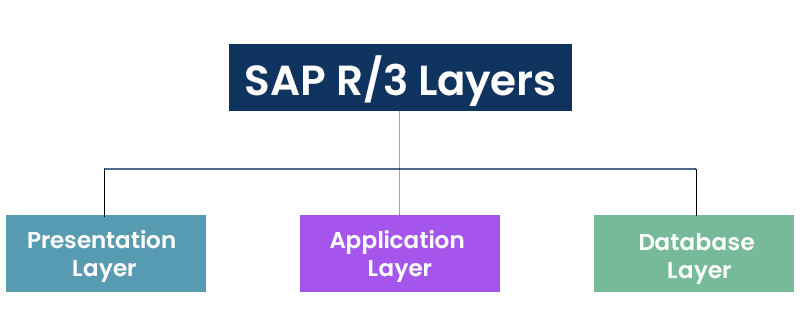
- Explain SAP R/3.
SAP R/3 is defined as the third-generation set of integrated software modules. It is known as one of the superior products in SAP, in which the R represents RealTime and the number 3 represents three-tier applications architecture.
SAP R/3 is an organization-wide information system that is primarily designed to coordinate all the resources, activities, and information needed to complete processes of common business, like human resource management, billing, order fulfillment, and production planning. SAP R/3 can be used by any organization despite the differences in its operations. SAP R/3 is of 3 primary layers:
- Presentation Layer: This layer consists of the software’s components, which are made of SAP GUI (Graphical User Interface). The presentation layer’s responsibility is to send the user’s input to the application server and to receive the data.
- Application Layer: The application layer consists of single/ multiple application servers and a message server. The message server is used to transmit the request from one application server to another within the system. Additionally, it holds information related to application server groups and the current load balancing within them. This will use this information to assign a suitable server when a user logs into the system.
- Database Layer: The database layer consists of a central database system that contains all the data in the R/3 System. SAP has developed a database named HANA, but this database is compatible with many databases like Oracle.
Some sap interview questions and answers will be in the form of differentiation. One such question is given below.
- State the differences between OLAP and Data Mining.
| Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) | Data Mining |
| OLAP functions as a reporting tool employed to acquire an understanding of database schema, dimensions, and the makeup of facts (values and attributes). | OLAP functions as a reporting tool employed to acquire an understanding of database schema, dimensions, and the makeup of facts (values and attributes). |
| It is employed to analyze past data. | It is employed to analyze past data. |
| It handles intricate transaction-level data. | It handles intricate transaction-level data. |
| This approach to data analysis adopts a top-down methodology, where insights are derived from the examination of the larger context. | This approach to data analysis adopts a top-down methodology, where insights are derived from the examination of the larger context. |
- State difference between Salesforce and SAP.
| Salesforce | SAP |
| Salesforce presents a holistic CRM (Customer Relationship Management) tool encompassing all features within a unified plan while also offering various products and software solutions to cater to both developers and users. | SAP CRM stands out as a highly demanded ERP software, providing a versatile array of tools suitable for businesses across a wide spectrum of industries. It empowers users to pick and choose the functions they need. |
| Salesforce exclusively employs a Cloud-based deployment model and does not endorse On-premise deployment options. | SAP employs a cloud-based deployment model and extends support for On-premise deployment as well. |
| An extra fee is required to access the Salesforce CRM’s premium features. | With SAP, there are no extra charges, and the cost entails annual fees for licensing, maintenance, and support. |
| Customers receive the “Get Started” guide as part of their subscription package; however, additional guides or customization training must be purchased separately. | Users are required to make separate purchases to access online training modules and certification in SAP. |
- State the Difference between Open and Native SQL.
| Open SQL | Native SQL |
| Open SQL consists of ABAP-specific (Cross-database) SQL statements. | Native SQL consists of database-specific SQL statements. |
| Open SQL can operate only on tables that are created in the ABAP dictionary(SE11). | Native SQL is used on the database tables which are not being administered by the ABAP dictionary |
| Open SQL will support the buffering of tables in an SAP Application server. | Native SQL won’t support for buffering of tables in the SAP Application server |
| Open SQL will support conjunction with ABAP constructions that simplify or speed up access. | Native SQL won’t support conjunction with ABAP constructions that simplify or speed up access |
In conclusion, SAP is one of the most demanded software that is used to efficiently manage a company’s resources. A significant benefit of adopting SAP is its exceptionally high level of integration among its applications, guaranteeing data consistency across both the system and the organization. In this blog, we delved into the scope of SAP and sap interview questions and answers.